Dead or Alive Technology
Motherboards & RAM QVL: Why Compatibility Matters
Table of Contents
Categories
Share This Post

When building or upgrading a PC, choosing the right RAM for your motherboard is crucial. Many users assume that as long as the RAM type (DDR4, DDR5, etc.) matches the motherboard’s specifications, it will work seamlessly. However, this isn’t always the case. This is where the Qualified Vendor List (QVL) comes into play. Ignoring the QVL can lead to system instability, crashes, or failure to boot.
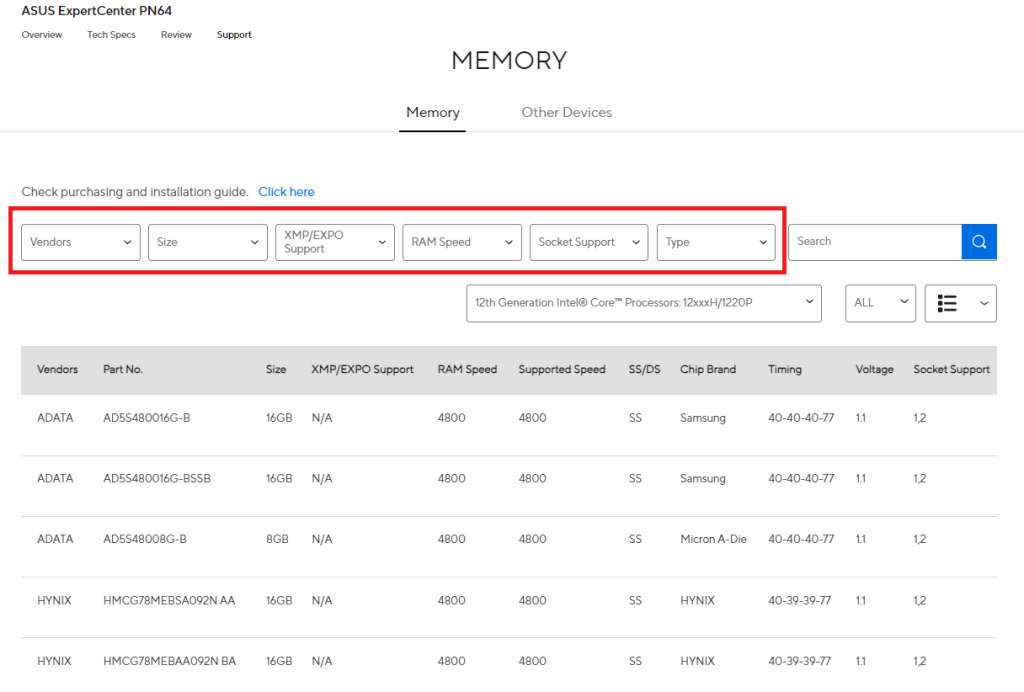
What is a Motherboard’s QVL?
The Qualified Vendor List (QVL) is a list provided by the motherboard manufacturer that details RAM modules that have been tested and confirmed to work with that specific motherboard model. The QVL is typically found on the motherboard’s official product page under the support or downloads section.
Manufacturers test RAM kits from different brands (such as Corsair, G.Skill, Kingston, and Crucial) to ensure stability at the rated speeds, timings, and voltages. If a RAM module appears on the QVL, it means the motherboard’s BIOS has been optimized for that specific module, ensuring smooth operation.
Why is the QVL Important?
While motherboards are designed to support a range of RAM speeds and capacities, the QVL helps avoid compatibility issues by ensuring the following:
- Guaranteed Compatibility: The listed RAM has been physically tested to work with the motherboard.
- Stable Performance: RAM kits on the QVL are verified to run at their advertised speeds without causing system crashes or instability.
- Fewer Troubleshooting Headaches: Using RAM that is not on the QVL increases the chances of random system crashes, memory errors, or even failure to boot.
Risks of Using Newer RAM Modules Not on the QVL
One of the challenges with RAM compatibility arises when newer RAM modules are released after a motherboard has been manufactured. Since motherboard manufacturers cannot test RAM that did not exist at the time of production, using newer RAM carries some risks:
- BIOS Incompatibility: Older BIOS versions may not recognize the memory properly, leading to boot failures or defaulting to lower speeds.
- XMP Profile Issues: Newer RAM may have XMP (Extreme Memory Profile) settings that are not optimized for older motherboards, causing stability issues when enabled.
- Latency & Voltage Mismatches: Even if a newer RAM kit has the same frequency as an older one, differences in memory timings and voltages could lead to instability or failure to post.
- Limited Speed Support: Some motherboards may not fully support the speeds of newer RAM kits, causing them to run at lower-than-advertised frequencies.
How to Minimize Compatibility Issues
If you’re considering installing newer RAM on an older motherboard, follow these steps to reduce the risk of issues:
- Check the Motherboard’s QVL – If the RAM is on the QVL, you’re in the clear.
- Update the BIOS – Motherboard manufacturers often release BIOS updates that improve memory compatibility.
- Research User Reports – Check forums and reviews to see if other users have successfully used your chosen RAM with the same motherboard.
- Manually Adjust Settings – If the RAM isn’t stable, tweaking voltages, timings, or disabling XMP in the BIOS may help.
- Buy from Reputable Brands – Some memory manufacturers work closely with motherboard vendors to ensure their modules function well, even if they are not explicitly listed on the QVL.
Conclusion
The motherboard’s Qualified Vendor List (QVL) is an essential reference when selecting RAM to ensure system stability and optimal performance. While newer RAM modules may work with older motherboards, there is always a risk of compatibility issues. If you’re upgrading memory, checking the QVL, updating your BIOS, and doing research can save you from potential headaches. Choosing the right RAM isn’t just about speed—it’s about compatibility.
